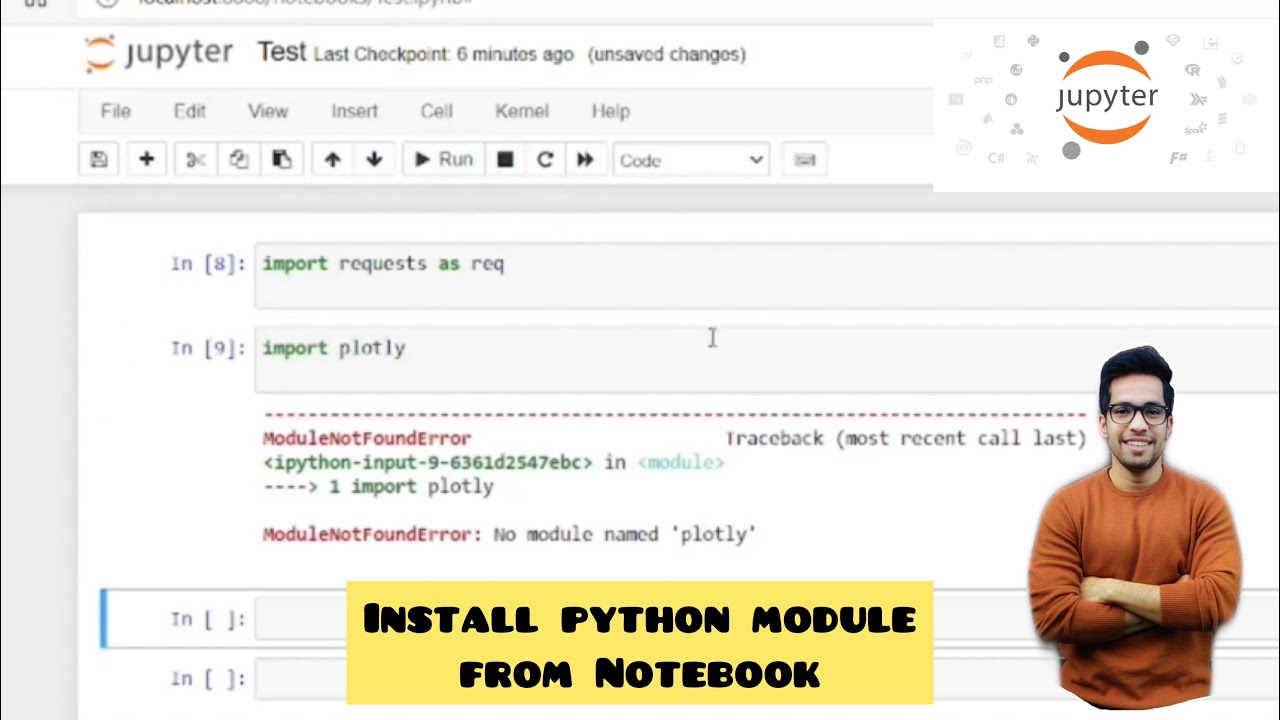
How to solve modulenotfounderror no module named ‘cron-descriptor’ in python
Understanding Python Module Errors
Python is a versatile programming language that has gained immense popularity among developers. However, like all programming languages, it can sometimes present challenges, particularly when it comes to module management. One common issue developers face is the ModuleNotFoundError. This error typically indicates that a specified module cannot be found, which can halt your project’s progress.
When you encounter the error message stating that there is “No module named ‘cron-descriptor’”, it usually means that the module has not been installed, or there is a typo in the module name. A popular package, cron-descriptor, is used for parsing crontab expressions in a user-friendly manner, and it’s essential for specific applications that schedule tasks.
Why You Might Encounter the ‘cron-descriptor’ Module Error
There are several reasons why you might face the error related to cron-descriptor when working with Python:
- Module Not Installed: The most common reason for this error is that the cron-descriptor module is not installed in your Python environment.
- Virtual Environment Issues: If you’re using a virtual environment, it’s possible that cron-descriptor is not installed within that specific environment.
- Incorrect Python Version: Sometimes, packages are only available for specific Python versions. Ensure that you are using a compatible version of Python.
- Typographical Errors: Errors in the module name when importing can lead to this issue. Always double-check the spelling.
How to Solve ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘cron-descriptor’
If you find yourself facing this particular module error, don’t worry! The solution is straightforward. Below is a step-by-step guide to fixing the ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘cron-descriptor’.
Step 1: Install the Module
The first step to resolving the error is to install the cron-descriptor module using Python’s package manager, pip. You can do this by running the following command in your terminal:
pip install cron-descriptorEnsure that you are connected to the internet and that you have the appropriate permissions to install packages. If you are using a virtual environment, ensure it is activated before running the command.
Step 2: Verifying Installation
After installation, it’s crucial to verify that the module has been successfully installed. You can check this by running the following command:
pip show cron-descriptorThis command will display information about the installed module, including its version. This confirms that the installation was successful and the module is available for use.
Step 3: Importing the Module
Once you have verified the installation, you can now try importing the module in your Python script:
import cron_descriptor
If you do not see any errors upon running this import statement, you have successfully resolved the ModuleNotFoundError related to the cron-descriptor module.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Despite following the steps above, you may still encounter errors. Here are some common troubleshooting tips:
- Ensure that you are using the correct Python executable. You can check this by running which python or where python depending on your operating system.
- Check if the cron-descriptor module is installed in the correct Python environment by listing installed packages using pip list.
- If you are using an IDE or code editor, make sure it is set to use the right Python interpreter.
Best Practices for Managing Python Modules
Managing Python modules efficiently can help you avoid encountering module errors in the future. Here are some best practices:
Use Virtual Environments
Virtual environments are isolated spaces to manage your project’s dependencies without affecting your system’s global packages. Always create a virtual environment when starting a new project. You can create one using:
python -m venv myproject_envThis command creates a new virtual environment named myproject_env. Activate it and install all necessary packages within this environment.
Regularly Update Your Packages
Ensuring that your packages are up-to-date can prevent compatibility issues. You can update your packages using the following command:
pip install --upgrade cron-descriptorThis command will ensure that you have the latest version of cron-descriptor, which may contain bug fixes or improvements.
Document Your Dependencies
Keep track of your project’s dependencies by creating a requirements.txt file. You can generate it using:
pip freeze > requirements.txtThis file will make it easier to install all necessary packages in new environments or when sharing your project. Anyone can install the required packages with:
pip install -r requirements.txtUnderstanding the Importance of Cron-Descriptor
Before delving further into the functionalities of the cron-descriptor module, it is essential to understand why it is critical for many programmers. The cron-descriptor module provides a way to transform cron expressions into human-readable formats, making it invaluable for applications that require task scheduling.
Applications of Cron-Descriptor
There are many scenarios in which cron-descriptor can be très useful:
- Monitoring Scheduled Tasks: It helps developers visualize the schedule of various tasks running in the background, facilitating easier debugging and maintenance.
- User Interface Development: By converting cron expressions to human-readable formats, developers can create user interfaces where users can easily understand when tasks are scheduled.
- Documentation and Reporting: Clear documentation on scheduling can be generated for reports, assisting in clarity and transparency.
Using Cron-Descriptor Effectively
To make the best use of the cron-descriptor module, it’s essential to understand how to correctly define cron expressions. A cron expression is a string composed of five or six fields separated by spaces, used to specify a schedule for running commands. Each field can have different values:
- Minute: 0-59
- Hour: 0-23
- Day of Month: 1-31
- Month: 1-12
- Day of Week: 0-7 (where both 0 and 7 represent Sunday)
- Year (optional): 1970-2099
For example, a cron expression like “0 5 * * *” indicates the task will be executed every day at 5 AM. The cron-descriptor can transform this expression into a user-friendly format such as “Every day at 5:00 AM.”
Leveraging Community Resources
Python has a robust online community that creates a wealth of **resources** for both beginners and seasoned developers. Engaging with the community can significantly enhance your proficiency with modules like cron-descriptor. Here are some ways to leverage community resources:
Participate in Forums and Discussion Groups
Websites like Stack Overflow and Reddit have dedicated sections where developers discuss common problems, solutions, and share knowledge regarding various Python modules. Joining these discussions can provide you with insights into best practices and troubleshooting tips.
Explore Online Documentation and Tutorials
Always refer to the official documentation for any module you are using. The documentation for cron-descriptor provides detailed instructions on how to implement and use its features. Additionally, there are many online tutorials that guide you through practical examples that can help you understand the module better.
Contribute to Open Source Projects
Engaging with open source projects can also deepen your understanding of Python modules. By contributing to projects that utilize cron-descriptor, you will not only enhance your coding skills but also familiarize yourself with how the module is used in real applications. Platforms like GitHub are excellent places to find projects that might use this module.