How to solve ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘pytest-metadata’ in Python
Understanding ModuleNotFoundError
Python is a powerful programming language that is known for its simplicity and versatility. However, developers often encounter various errors during their coding journey. One of the most common issues you might face is the ModuleNotFoundError, specifically, the error stating No module named ‘pytest-metadata’. This error typically arises when Python is unable to locate the requested module in your environment.
To grasp this error better, let’s first explore how Python manages dependencies and modules. Python relies on a system called **PyPI** (Python Package Index) to install and manage external libraries. When you try to import a module that is not installed, this is where the ModuleNotFoundError comes into play.
Common Causes of ModuleNotFoundError
There are several reasons why you might encounter the ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘pytest-metadata’. Understanding these reasons is crucial for effectively debugging your code. Here are some of the most common causes:
- The module is not installed: This is the most straightforward reason. If you haven’t installed the module, Python obviously won’t find it.
- Virtual environment issues: If you’re using a virtual environment and the module is not installed there, you will encounter this error.
- Python version mismatch: Sometimes, the module might not be available for the version of Python you are using.
- Typographical errors: A simple typo in the module name during the import can lead to this error.
Identifying the root cause will allow you to adopt an effective solution.
How to Fix the Error: No module named ‘pytest-metadata’
If you are looking for a solution to the ModuleNotFoundError, particularly for the missing ‘pytest-metadata’ module, here’s what you can do:
Step 1: Installing the Missing Module
The most common way to resolve the error is to install the missing module. You can do this using the Python package manager called pip. Open your terminal or command prompt and run the following command:
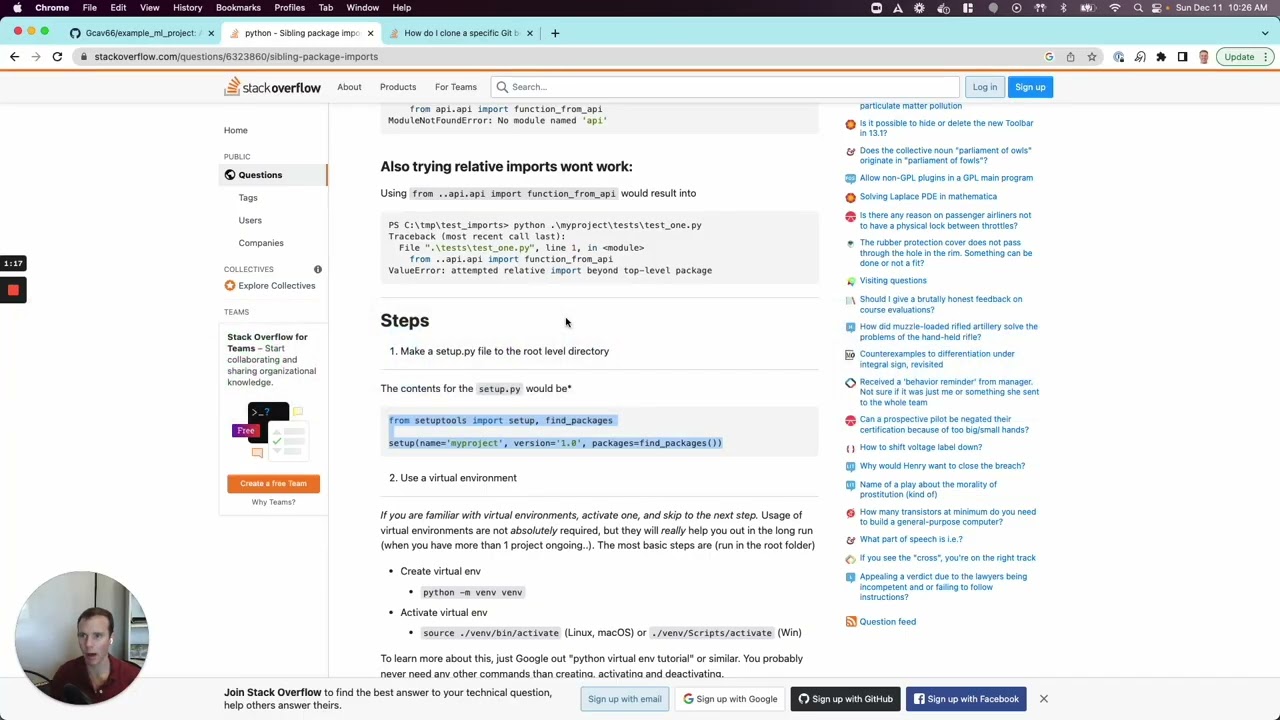
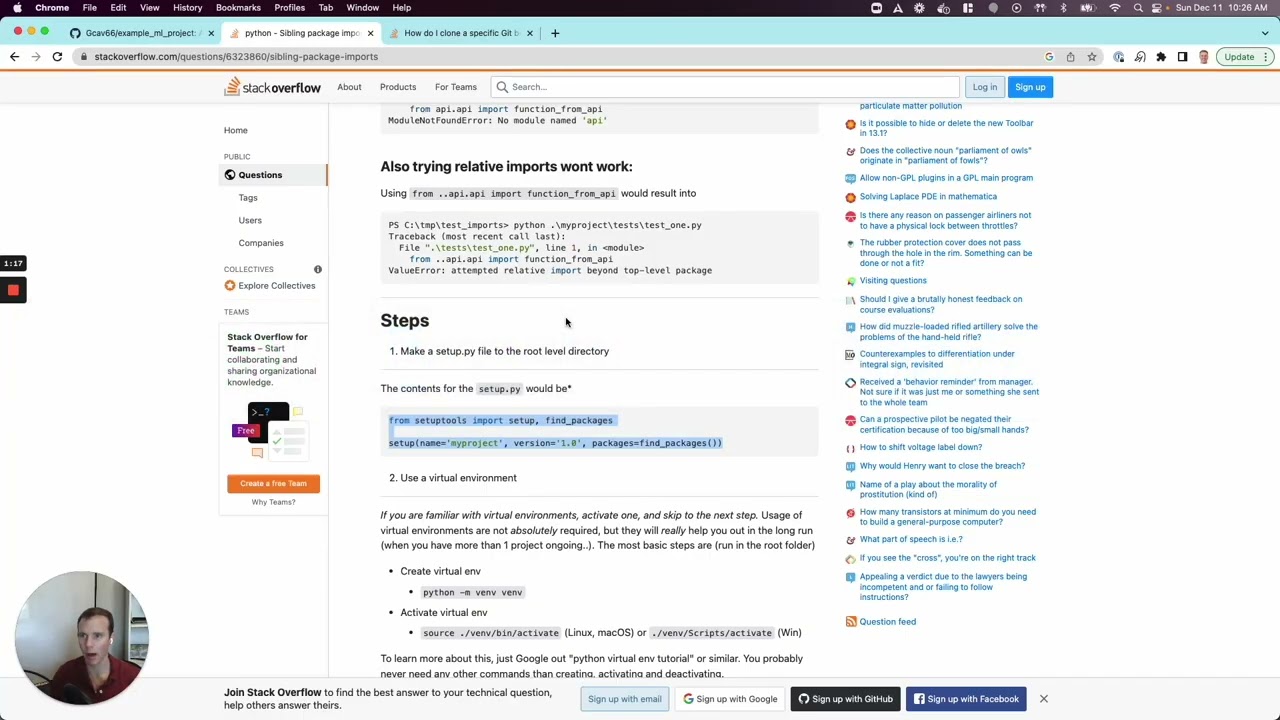
pip install pytest-metadataThis command will fetch the pytest-metadata module from the PyPI repository and install it for your current Python environment. Make sure you have an active internet connection for this operation.
Step 2: Verify Your Virtual Environment
If you are using a virtual environment, ensure that the module is installed within that environment. To activate your virtual environment, run:
source env/bin/activate # On macOS/Linux
envScriptsactivate # On WindowsOnce activated, you can verify if pytest-metadata is installed by running:
pip listThis command lists all the installed packages in your current environment. If you don’t see pytest-metadata, run the install command again.
Step 3: Check Your Python Version
It’s important to ensure that you’re using a compatible version of Python where pytest-metadata is supported. You can check your Python version using:
python --versionMake sure you are working in a compatible version that aligns with your project requirements. Many libraries drop support for older Python versions, which could be a reason for the error.
Step 4: Debugging Your Imports
If you’ve verified that the module is installed, yet the error persists, check your import statements for any typos. Ensure you’ve written it correctly like so:
import pytest_metadataSimple mistakes in spelling can lead to the ModuleNotFoundError.
The Importance of Dependency Management
Now that you know how to fix the ModuleNotFoundError associated with ‘pytest-metadata’, it’s equally important to implement good practices for managing dependencies in your projects:
Use a Requirements File
It’s wise to maintain a requirements.txt file in your project directory. This file contains a list of all the packages your project depends on. You can create or update this file using:
pip freeze > requirements.txtWhen someone else wants to set up your project, they can install all dependencies in one command:
pip install -r requirements.txtRegularly Updating your Dependencies
Outdated modules can lead to compatibility issues. Regularly update your dependencies with:
pip install --upgrade pytest-metadataThis will ensure you have the latest features and security fixes.
Environment Isolation
Always utilize virtual environments, such as venv or virtualenv, to isolate your project dependencies. This helps ensure that each project can maintain its specific package versions without interfering with others.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Resolving ModuleNotFoundError
While resolving the ModuleNotFoundError can be straightforward, some common mistakes can lead to unnecessary headaches:
- Not using the correct version of pip: If you have multiple versions of Python installed, ensure you are using the right pip. Use
python -m pip install pytest-metadatato make sure you are installing it for the version of Python you want. - Ignoring the virtual environment: Always check if you are in the correct virtual environment before installing packages.
- Outdated package repository: Ensure your package index is updated by running
pip install --upgrade pipbefore installing packages.
Additional Resources for Managing Python Dependencies
For further exploration and better management of Python packages, consider the following resources:
- Python Packaging User Guide – A comprehensive guide on packaging and dependency management.
- Real Python Pipenv Guide – An introduction to using Pipenv for managing dependencies within Python projects.
- Python Packaging Authority – A resource for official Python packaging guidelines and insights.
By understanding these concepts and implementing best practices, you can navigate your projects with greater ease and confidence while avoiding common pitfalls associated with module errors, particularly the notorious ModuleNotFoundError.